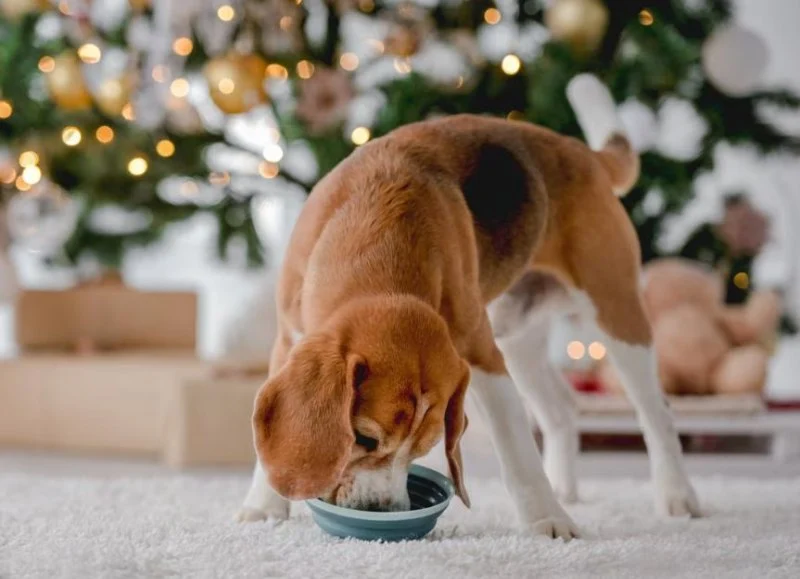

Managing Resource Guarding Behavior in Dogs: Practical Solutions for Pet Owners
- Understanding Resource Guarding in Dogs
- What Causes Resource Guarding Behavior?
- Recognizing the Signs of Resource Guarding
- Training Solutions to Manage Resource Guarding
- Real-Life Example: Overcoming Resource Guarding
- When to Seek Professional Help for Resource Guarding
1. Understanding Resource Guarding in Dogs
Resource guarding is a common behavior in dogs where they protect certain items or areas they consider valuable, such as food, toys, beds, or even people. This behavior can manifest in different ways, from growling or snapping to full-on aggression. It's essential to understand that resource guarding is a natural instinct for many dogs, but it can be problematic, especially if it escalates into aggressive behavior or leads to safety concerns.
While it’s often seen as a protective instinct, resource guarding can cause stress for both the dog and their owners. When not managed correctly, it can lead to tension, unsafe interactions, and even injuries. Understanding the behavior is the first step in addressing it effectively and helping your dog feel secure without resorting to aggression.
2. What Causes Resource Guarding Behavior?
Resource guarding in dogs typically stems from a variety of causes, often linked to the dog's early experiences and environment. Some of the primary factors include:
- Instinctive Behavior: Dogs naturally protect valuable resources as part of their survival instincts. This behavior is often seen in wild animals, where securing food or territory is critical.
- Insecurity or Fear: Dogs that are insecure or fearful may guard resources as a way to prevent perceived threats. This is especially common in dogs with a history of neglect or poor socialization.
- Lack of Socialization: Dogs that haven't been adequately socialized may struggle to understand how to interact safely with others around valuable resources, leading to defensive behavior.
- Past Experiences: If a dog has been deprived of resources in the past, they may develop a tendency to guard what they have out of fear of losing it again.
Understanding the root cause of your dog's resource guarding behavior is key to determining the best approach to managing it effectively. In some cases, the behavior may improve with training, while other dogs may require additional intervention.
3. Recognizing the Signs of Resource Guarding
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of resource guarding early so you can address the issue before it escalates. Signs of resource guarding include:
- Growling or Snapping: A dog may growl, snap, or show their teeth when someone approaches their food or belongings.
- Stiffening or Freezing: A dog may stiffen up or freeze when another dog or person gets too close to a valuable resource.
- Protective Posture: The dog may stand over or move closer to the resource to block access to it.
- Chasing or Blocking: A dog may chase away people or other pets who come near their guarded item or space.
If you notice any of these signs, it's crucial to take action to prevent the behavior from worsening. Early intervention with training can help reduce the intensity of the guarding behavior and improve your dog’s overall behavior around resources.
4. Training Solutions to Manage Resource Guarding
Managing resource guarding in dogs requires patience, consistency, and the right training techniques. Below are some effective methods to help curb this behavior:
- Desensitization and Counter-Conditioning: This technique involves gradually getting your dog used to the presence of people or other pets near their resources. Start by standing at a distance and slowly moving closer, rewarding your dog with treats for calm behavior. Over time, the dog will associate people approaching their resources with positive experiences rather than threats.
- Trade Games: Teaching your dog to "trade" an item, such as a toy or treat, for something of higher value can help reduce the instinct to guard. For example, offer a tastier treat when your dog drops their food, reinforcing that giving up a resource leads to a reward.
- Boundary Training: Teaching your dog to respect boundaries is crucial for reducing guarding behavior. For example, use commands like “leave it” to prevent your dog from fixating on or guarding an item.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog with praise and treats for calm behavior when they allow you or others to approach their food or toys without showing signs of guarding. This will reinforce the behavior you want to see.
Training should be done in a calm, controlled manner to avoid putting your dog in a situation where they feel threatened or overwhelmed. Consistency is key, and it may take time for the dog to fully adjust to the changes.
5. Real-Life Example: Overcoming Resource Guarding
Take the story of Bella, a two-year-old Labrador who had severe resource guarding tendencies around her food bowl. Bella would growl and snap whenever anyone tried to approach her while eating. Her owner, Mark, was concerned that this behavior could become dangerous, especially around children or guests.
Mark decided to implement some of the training techniques mentioned earlier. He started by desensitizing Bella to his presence during meal times, rewarding her for calm behavior when he approached her bowl. He also worked on teaching her a "leave it" command, using high-value treats as a reward for obeying the command.
Over the course of several weeks, Bella’s behavior improved significantly. She learned to associate Mark's presence near her food with positive rewards, and the growling and snapping eventually stopped. This success story shows how with the right approach, resource guarding behavior can be managed effectively and safely.
6. When to Seek Professional Help for Resource Guarding
If you’re unable to manage your dog’s resource guarding behavior with at-home training, or if the behavior escalates to aggressive outbursts, it may be time to seek professional help. A certified dog trainer or a veterinary behaviorist can work with you and your dog to develop a personalized training plan that addresses the specific issues your dog is facing.
In some cases, underlying health issues can exacerbate aggressive behavior, so it's essential to consult with a veterinarian to rule out any medical causes. Working with professionals can provide additional support and ensure that you are addressing the issue in a safe and effective manner.








 Princeton Veterinary Hospital4.0 (821 reviews)
Princeton Veterinary Hospital4.0 (821 reviews) Thomas Ridge Kennels4.0 (17 reviews)
Thomas Ridge Kennels4.0 (17 reviews) All Creatures Animal Hospital4.0 (354 reviews)
All Creatures Animal Hospital4.0 (354 reviews) Fatty Paws Pet Boutique0.0 (0 reviews)
Fatty Paws Pet Boutique0.0 (0 reviews) CityVet | Lone Mountain Veterinary & Urgent Care4.0 (104 reviews)
CityVet | Lone Mountain Veterinary & Urgent Care4.0 (104 reviews) Petnificent Picks5.0 (1 reviews)
Petnificent Picks5.0 (1 reviews) How to Transition a Senior Pet to Easier-to-Eat Food: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Transition a Senior Pet to Easier-to-Eat Food: A Comprehensive Guide The Hidden Dangers in Common Pet Supplies: What You Need to Know
The Hidden Dangers in Common Pet Supplies: What You Need to Know Managing Chronic Conditions in Pets: Essential Diet, Medication & Lifestyle Tips
Managing Chronic Conditions in Pets: Essential Diet, Medication & Lifestyle Tips How to Build a Pet Emergency Kit: Essentials You Need
How to Build a Pet Emergency Kit: Essentials You Need Best Practices for Pet Grooming Frequency by Breed: Keeping Your Pet’s Coat Healthy
Best Practices for Pet Grooming Frequency by Breed: Keeping Your Pet’s Coat Healthy The Effect of Seasonal Allergies on Pets & How to Help
The Effect of Seasonal Allergies on Pets & How to Help