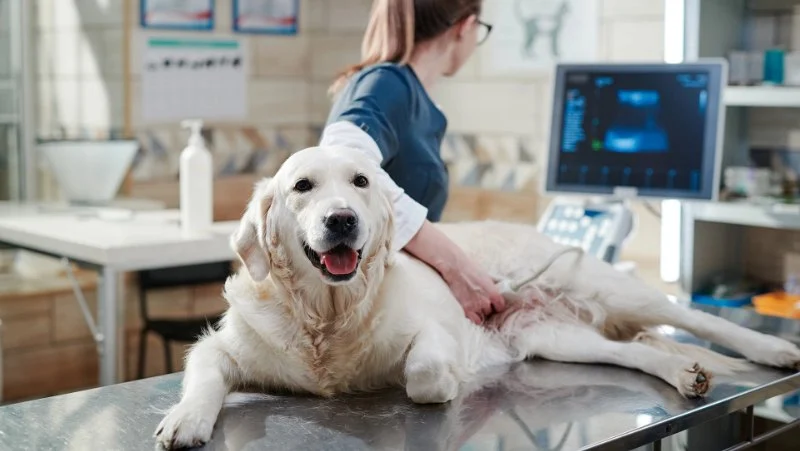

3D Imaging & Pet Diagnostics: What You Should Know
- Understanding 3D Imaging in Pet Diagnostics
- Benefits of 3D Imaging for Pet Health
- How 3D Imaging Works in Veterinary Medicine
- Applications of 3D Imaging in Pet Diagnostics
- Real-Life Examples of 3D Imaging in Action
- The Future of Pet Diagnostics with 3D Imaging
1. Understanding 3D Imaging in Pet Diagnostics
3D imaging technology has revolutionized pet diagnostics, offering a more accurate and detailed view of a pet's internal health. Unlike traditional X-rays or 2D imaging techniques, 3D imaging creates detailed, three-dimensional models of a pet’s body, providing veterinarians with a better understanding of complex medical issues. This technology allows for a more comprehensive examination of organs, bones, and tissues, which can be crucial in diagnosing conditions that may be missed with conventional methods.
Veterinarians use advanced imaging systems, such as CT (computed tomography) scans and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), to create 3D images of your pet’s body. These images offer a higher level of clarity, helping vets make more precise diagnoses and improve treatment outcomes.
2. Benefits of 3D Imaging for Pet Health
3D imaging technology offers numerous benefits that enhance the care of pets and the diagnostic process. Here are some key advantages:
- Increased Accuracy: 3D imaging provides a more accurate representation of internal structures, leading to better-informed decisions about treatment plans.
- Non-Invasive: Unlike surgery, 3D imaging is a non-invasive technique, meaning there is no need for incisions or cutting into the pet’s body, reducing the risk of infection and recovery time.
- Better Visualization of Complex Areas: With 3D imaging, veterinarians can examine areas that are difficult to see with traditional methods, such as the spine, joints, and soft tissues.
- Early Detection of Health Issues: By providing detailed images, 3D imaging allows for the early detection of health problems, such as tumors, fractures, or heart abnormalities, that may not be visible through routine physical exams.
- Improved Treatment Planning: With clearer images of a pet’s internal anatomy, vets can plan surgeries, therapies, or other interventions more effectively, improving the chances of successful outcomes.
Overall, 3D imaging empowers veterinarians to provide a higher standard of care, enhancing the diagnosis and treatment of pets.

Nurture Animal Clinic
3070 Batavia-Williamsburg Pike, Batavia, OH 45103, USA
3. How 3D Imaging Works in Veterinary Medicine
In veterinary medicine, 3D imaging typically involves advanced scanning techniques such as CT and MRI, which use different methods to capture detailed images of your pet’s body.
CT Scans: CT scans use X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of your pet’s body. These images are then compiled into a 3D model, providing an in-depth view of bones, organs, and other structures. CT scans are especially useful for examining bone fractures, tumors, and abnormalities in the chest and abdominal area.
MRI: MRI technology uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, and muscles. Unlike CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for pets in certain situations. MRIs are commonly used to diagnose neurological issues, joint problems, and soft tissue injuries.
Both CT and MRI technologies work in conjunction to offer a comprehensive diagnostic tool that helps veterinarians assess both bone and soft tissue health, ensuring that no potential issue is overlooked.
4. Applications of 3D Imaging in Pet Diagnostics
3D imaging technology has a wide range of applications in veterinary diagnostics, assisting in the identification and treatment of various conditions. Here are a few areas where 3D imaging is particularly beneficial:
- Orthopedic Issues: 3D imaging is invaluable in diagnosing bone fractures, joint issues, and deformities. It allows veterinarians to see the extent of fractures or the alignment of bones, helping them plan surgeries or treatments more effectively.
- Neurological Disorders: For pets with neurological symptoms, such as seizures, weakness, or paralysis, 3D imaging provides detailed images of the brain and spine, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, or herniated discs.
- Cancer Detection: 3D imaging is useful for detecting tumors, both benign and malignant, and for monitoring their progression. Early detection through 3D imaging can lead to more effective treatment and higher survival rates for pets diagnosed with cancer.
- Cardiovascular Health: By providing a clear view of the heart and blood vessels, 3D imaging allows for the diagnosis of heart disease, congenital defects, or other cardiovascular issues in pets.
- Dental Health: Dental problems are common in pets, and 3D imaging can be used to identify dental issues that may not be visible with a traditional exam, such as tooth root abscesses or periodontal disease.
As veterinary technology continues to evolve, 3D imaging will play an increasingly important role in diagnosing and treating a wide variety of pet health conditions.
5. Real-Life Examples of 3D Imaging in Action
Consider the case of Max, a dog who had been limping for several weeks. Traditional X-rays did not reveal any fractures or significant issues, but after a CT scan, veterinarians discovered a small, previously undetectable fracture in his leg. With this information, they were able to treat Max’s condition with a more targeted approach, ultimately leading to a faster recovery.
In another case, a cat named Bella was suffering from unexplained weight loss and lethargy. An MRI revealed a brain tumor, a diagnosis that was only possible through 3D imaging. Early intervention allowed Bella’s owners to provide her with the best possible care, improving her quality of life and extending her time with her family.
These real-life cases highlight how 3D imaging can uncover hidden health problems that would otherwise go unnoticed, enabling timely and more effective treatment for pets.
6. The Future of Pet Diagnostics with 3D Imaging
The future of pet diagnostics is bright, with 3D imaging technology continuing to evolve. As advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are integrated with imaging technology, veterinarians will be able to analyze diagnostic images more quickly and accurately, improving the speed and precision of diagnoses.
In addition, the development of portable 3D imaging devices could make these advanced diagnostic tools more accessible, allowing for faster on-site evaluations in emergency situations or rural veterinary practices.
As 3D imaging technology becomes more refined and widely available, it will undoubtedly continue to transform the way veterinarians care for pets, offering better outcomes and a higher quality of life for animals.







 Princeton Veterinary Hospital4.0 (821 reviews)
Princeton Veterinary Hospital4.0 (821 reviews) Thomas Ridge Kennels4.0 (17 reviews)
Thomas Ridge Kennels4.0 (17 reviews) All Creatures Animal Hospital4.0 (354 reviews)
All Creatures Animal Hospital4.0 (354 reviews) Fatty Paws Pet Boutique0.0 (0 reviews)
Fatty Paws Pet Boutique0.0 (0 reviews) CityVet | Lone Mountain Veterinary & Urgent Care4.0 (104 reviews)
CityVet | Lone Mountain Veterinary & Urgent Care4.0 (104 reviews) Petnificent Picks5.0 (1 reviews)
Petnificent Picks5.0 (1 reviews) How to Transition a Senior Pet to Easier-to-Eat Food: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Transition a Senior Pet to Easier-to-Eat Food: A Comprehensive Guide The Hidden Dangers in Common Pet Supplies: What You Need to Know
The Hidden Dangers in Common Pet Supplies: What You Need to Know Managing Chronic Conditions in Pets: Essential Diet, Medication & Lifestyle Tips
Managing Chronic Conditions in Pets: Essential Diet, Medication & Lifestyle Tips How to Build a Pet Emergency Kit: Essentials You Need
How to Build a Pet Emergency Kit: Essentials You Need Best Practices for Pet Grooming Frequency by Breed: Keeping Your Pet’s Coat Healthy
Best Practices for Pet Grooming Frequency by Breed: Keeping Your Pet’s Coat Healthy The Effect of Seasonal Allergies on Pets & How to Help
The Effect of Seasonal Allergies on Pets & How to Help